Do I Need Host Public Key Before Generating User Ssh
- Do I Need Host Public Key Before Generating User Ssh Download
- Do I Need Host Public Key Before Generating User Ssh Download
- Do I Need Host Public Key Before Generating User Ssh Code
- Public Key Definition
- Symmetric Key
- Nov 10, 2011 How to Generate A Public/Private SSH Key Linux By Damien – Posted on Nov 10, 2011 Nov 18, 2011 in Linux If you are using SSH frequently to connect to a remote host, one of the way to secure the connection is to use a public/private SSH key so no password is transmitted over the network and it can prevent against brute force attack.
- The user name is a comment, you can delete it or set it with the -C option. I do not see a host name anywhere in the keys, what file are you looking at? Ssh-keygen -f test -C noname Generating public/private rsa key pair. Enter passphrase (empty for no passphrase): Enter same passphrase again: Your identification has been saved in test.
- Set up public-key authentication using SSH on a Linux or macOS computer. To set up public-key authentication using SSH on a Linux or macOS computer: Log into the computer you'll use to access the remote host, and then use command-line SSH to generate a key pair using the RSA algorithm. To generate RSA keys, on the command line, enter: ssh-keygen -t rsa.
How Do I Generate SSH Keys? Published on: Tue, Sep 23, 2014 at 10:53 am EST. Paste in your SSH public key. This is a long string beginning with 'ssh-rsa'. Remember to select the keys before the initial server deployment, otherwise you will need to log into the newly created server and add the SSH keys. Dec 02, 2019 On the user’s side, the public SSH key is stored in an SSH key management software or in a file on their computer. Using SSH Keys First Steps. Before you can start using SSH keys, first you need to generate your own SSH key pair on the system you would like to use to access a remote system.
In order to use public and private key based authentication to SFTP to your server, you need to have SSH enabled on your hosting account. Most hosts do not enable SSH by default, so you might want to check with your host and get it enabled if it isn't already. Once SSH is enabled, connecting to your server is simple. Here are three main steps involved:
- Generating public and private Key pairs using Cpanel.
- Downloading and converting the private key into PPK (PuTTY Private Key) format.
- Connecting to your server using an FTP client and using the PPK key for authentication.
So let's look at these steps in details:
Generating Public and Private Key Pairs Using Cpanel
In order to use SFTP, we first need to generate public and private key pairs. This can easily be done using Cpanel as detailed in the steps below:
Step 1:Login to Your Cpanel and click on SSH Shell Access under the security section.
Step 2: Click on the Manage SSH Keys button and then Click on the Generate a New Key link.
Step 3: On this page, enter the following details:
Key Password: Any password. (Note: This is the passpharse that you will need to enter while you SFTP.)
Key Type: RSA
Key Size: 2048
Once all details are entered, click on Generate Key (refer image above). This will generate a public and private key pair. You should now be able to see these files in your Manage SSH Keys page.
Step 4: On the Manage SSH Keys page, click on Manage Authorization and then click the Authorize button. This will authorize the key for usage as shown in the image below.
Do I Need Host Public Key Before Generating User Ssh Download
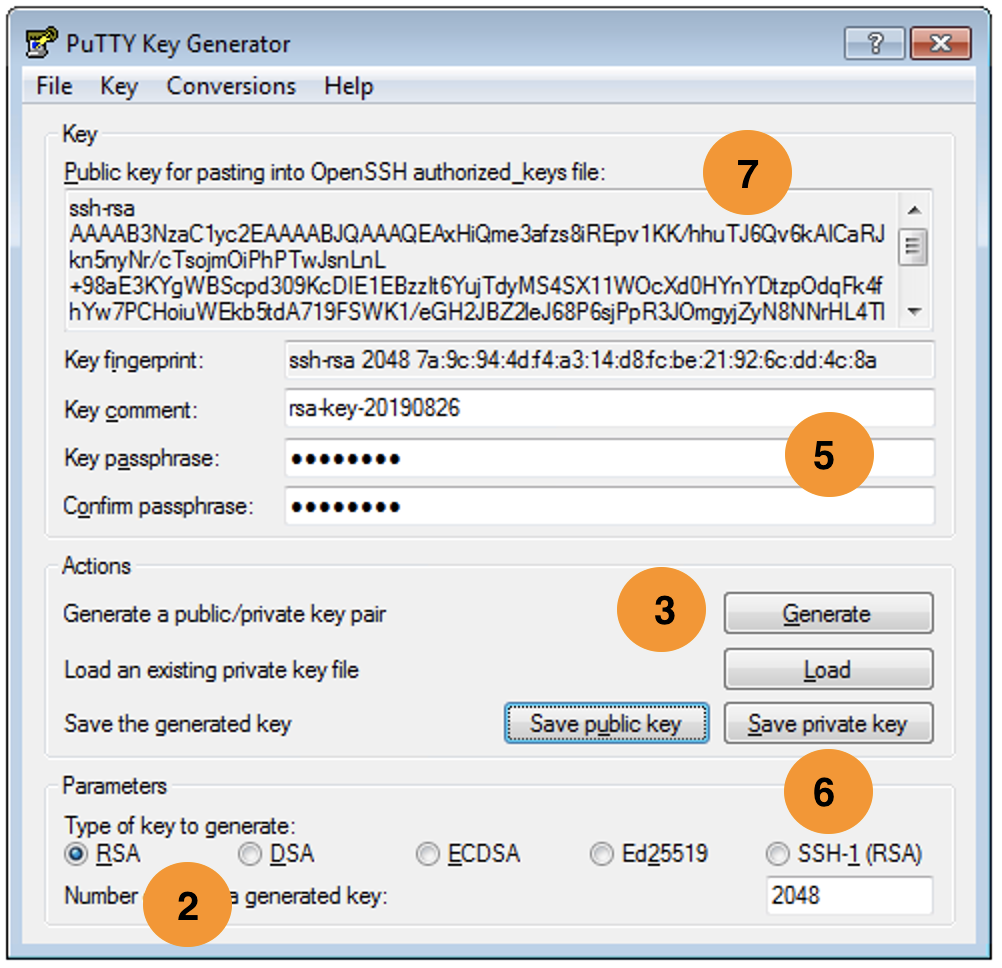
Step 5: Click on the View or Download link in the Private Keys section to covert and download your private key.
Converting Private Key to PPK Format
We now need to convert the private key to PPK format. You can do this using the covert key option on Cpanel, or you can download the raw file and covert it to PPK format using PuttyGen. In most cases, the Cpanel convert option works pretty good, so you can stick with it. But in-case, you don't have that option in your Cpanel account, you can use the Puttygen method. Let's look at both these methods:
Option 1: Converting the key to PPK format using Cpanel Covert key option:
To use this option, enter your passphrase in the space provided and click Convert as shown in the image below. You can then download the converted key to your computer and save it in an accessible location.
Note: The passpharse is the key password that you used while generating the keys in Cpanel.
Option 2: Converting the Key to PPK format Using PuttyGen:
This option involves using PuttyGen to convert the key. If you don't have PuttyGen installed, you can download it free from here. Once downloaded and installed, follow these steps:
Step 1: As shown in the image above (marked Option 2), click on the 'Download Key' button on the View or Download SSH Keys page. This will download the private key (id_rsa) to your computer. Copy and save this file in an accessible location.
Step 2: Open the PuttyGen application and click Run.
Step 3: Go to Conversions > Import Key, browse to the location of your downloaded private key file (id_rsa) and select the file.
Once you load the file you will be prompted to enter the passpharse. Enter the passpharse and click ok.
Step 4: Make sure that the SSH2 RSA option is selected and the number of bits is set to 2048.
Step 5: Click on Save private key and save the file with your preferred name. (Refer image above).
SFTP to the Server
Now that we have our public and private keys setup, we can SFTP to the server. You can do this using any FTP client like Filezilla or WinSCP. I am using WinSCP for this tutorial.
Step 1: Open WinSCP and create a new FTP connected by clicking on New Site and enter the following details:
Host Name: ftp.domainname.com
Port Number: 22
Username: Cpanel Username
Password: Cpanel Password
Step 2: Click on the Advanced botton to open the Advanced Site Settings page as shown in point no.6 in the image above.
Step 3: On the Advanced Site Settings page click on Authentication and then browse to the location of your PPk file. Refer image below:
Step 4: Once done, click ok and then click Save to save the settings.
Step 5: Click Login to login to your server using SFTP. Once the connection is establised and the server has finished verifing the private and public keys, you will be promoted to enter the passpharse. Enter the passpharse and click Ok.
You should now be connected to your server using SFTP.
Introduction
Establishing an SSH (Secure Shell) connection is essential to log in and effectively manage a remote server. Encrypted keys are a set of access credentials used to establish a secure connection.
This guide will walk you how to generate SSH keys on Ubuntu 18.04. We will also cover setting up SSH key-based authentication to connect to a remote server without requiring a password.
- A server running Ubuntu 18.04
- A user account with sudo privileges
- Access to a terminal window / command line (Ctrl-Alt-T)
If you are already running an Ubuntu 18.04 server, you can skip this step. If you are configuring your server for the first time, you may not have SSH installed.
Spore key code generator download. 1. Start by installing the tasksel package:
The system will first ask for confirmation before proceeding:
2. Next, use tasksel to install the ssh-server:
3. Load the SSH server service, and set it to launch at boot:
On your client system – the one you’re using to connect to the server – you need to create a pair of key codes.
To generate a pair of SSH key codes, enter the commands:
This will create a hidden directory to store your SSH keys, and modify the permissions for that directory. The ssh-keygen command creates a 2048-bit RSA key pair.
For extra security, use RSA4096:
If you’ve already generated a key pair, this will prompt to overwrite them, and those old keys will not work anymore.
The system will ask you to create a passphrase as an added layer of security. Input a memorable passphrase, and press Enter.
This process creates two keys. One is a public key, which you can hand out to anyone – in this case, you’ll save it to the server. The other one is a private key, which you will need to keep secure. The secure private key ensures that you are the only person who can encrypt the data that is decrypted by the public key.
Step 2- Copy Public Key to the Ubuntu Server
First, get the IP address of the Ubuntu server you want to connect to.
In a terminal window, enter:
The system’s IP address is listed in the second entry:
On the client system, use the ssh-copy-id command to copy the identity information to the Ubuntu server:
Replace server_IP with the actual IP address of your server.
Do I Need Host Public Key Before Generating User Ssh Download
If this is the first time you’re connecting to the server, you may see a message that the authenticity of the host cannot be established:
Do I Need Host Public Key Before Generating User Ssh Code
Type yes and press Enter.
The system will check your client system for the id_rsa.pub key that was previously generated. Then it will prompt you to enter the password for the server user account. Type it in (the system won’t display the password), and press Enter.
The system will copy the contents of the ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub from the client system into the ~/.ssh/authorized_keys directory of the server system.
The system should display:
Public Key Definition
If your system does not have the ssh-copy-id command, you can copy the key manually over the SSH.
Use the following command:
To log in to a remote server, input the command:
The system should not ask for a password as it is negotiating a secure connection using the SSH keys. If you used a security passphrase, you would be prompted to enter it. After you do so, you are logged in.

If this is the first time you’ve logged into the server, you may see a message similar to the one in part two. It will ask if you are sure you want to connect – type yes and press Enter.
Step 4- Disable Password Authentication
This step creates an added layer of security. If you’re the only person logging into the server, you can disable the password. The server will only accept a login with your private key to match the stored public key.
Edit the sshd_config file:
Search the file and find the PasswordAuthentication option.
Edit the file and change the value to no:
Save the file and exit, then restart the SSH service:
Verify that SSH is still working, before ending the session:
Symmetric Key
If everything works, you can close out and resume work normally.
By following the instructions in this tutorial, you have setup SSH-key-based authentication on an Ubuntu 18.04 server.
The connection is now highly secure as it uses a set of unique, encrypted SSH keys.
Next you should also read
Learn how to set up SSH key authentication on CentOS to safely communicate with remote servers. Create the…
When establishing a remote connection between a client and a server, a primary concern is ensuring a secure…
Nginx is an open-source server utility designed to work as a reverse proxy, intercepting client requests and…
In this tutorial, Find out How To Use SSH to Connect to a Remote Server in Linux or Windows. Get started with…